Electrode tip
Purpose and material quality
Electrode supplies a welding current to welding part, applies a pressure force, and cools surface of the work piece.
It needs to have good conductivity and thermal conductivity, and also high hardness and wear resistance.
It is important to control the tip shape of electrode for realizing the consistent welding quality, because a temperature rise decreases by reducing the current density of welding part and expanding the surface of a tip of electrode, generally a nugget size grows small while welding.
Shape of electrode
There are tip shapes of electrode being printed on this catalog. You can use them properly, due to the shape of work piece. Cap Tip type electrode which enables easy replacement of only a tip is often being used for material saving and cost reduction.
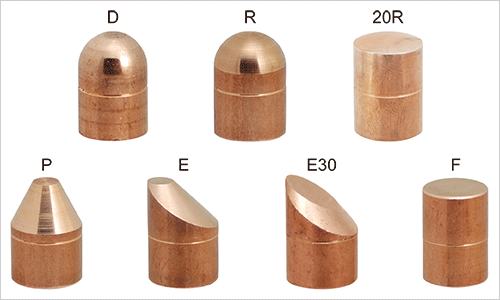
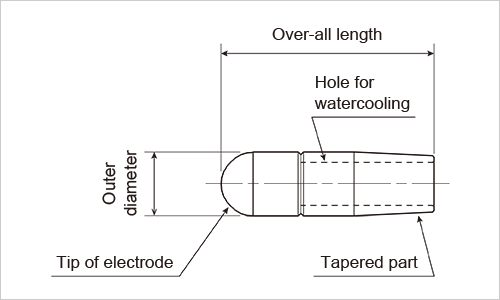
Built-in
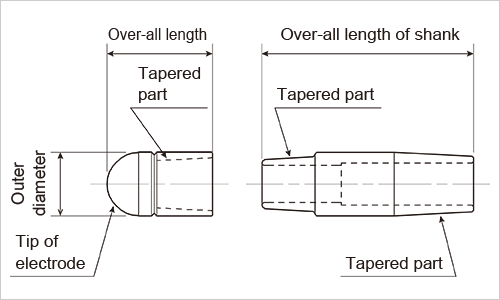
Cap tip type
A simple method of measuring taper
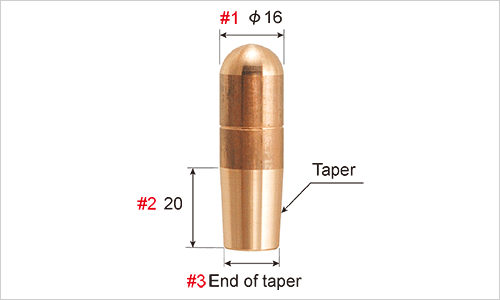
If #3 is approx. 14 mm, the taper is 1/10
If #3 is approx. 15 mm, the taper is MT#2 (Morse taper)
If #3 is approx. 12 mm, the taper is 1/5
This is simple measurement method. Please use it as a guide.
Control method of electrode
Lifetime of electrode
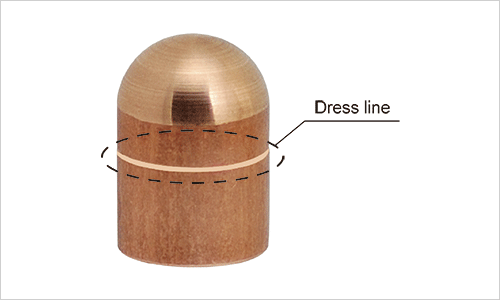
Lifetime of electrode in resistance welding is the most important control point and gives large influence on productivity by requiring frequent replacement of electrode changing (dressing). In case electrode is over the limit of used lifetime, poor weld will occur. Checking the condition of standard nugget diameter or whether the number of times is below standard shear strength, replace the tip of electrode tip or replace with new one, as a guide the times of the number is 0.5~0.7 times, which is equal to lifetime of an electrode.
Dressing and changing of electrode
Consequently, the contact resistance is increased.
It always needs that the initial state is restored by dressing the tip of electrode tip regularly on the way continuously welding. Because it is the cause of poor weld by increasing the area of the tip of electrode and decreasing current density although current is constant. In case of projection welding, parallelism between an upper electrode and a lower electrode is important.
Method for cooling electrode
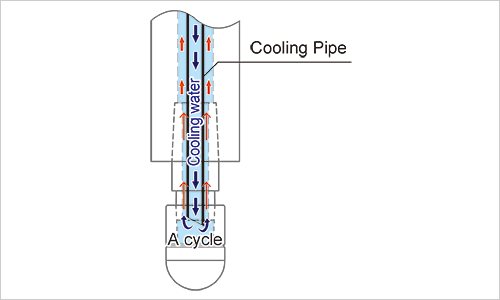
It is important to maintain circulating water temperature and flow rate jetting from water cooled tube inside an electrode in order to prolong life of an electrode and an equipment and realize consistent welding quality.
To maintain the temperature of circulating water at 10~30℃ and control the flow rate at 2~3 liters per minute for one electrode tip.
List of electrode materials
| Type | Electrical conductivity (%IACS) |
Hardness (HRB) |
Characteristics | Application example (Use) |
RWMA (CLASS) |
| Type 1 Cadmium copper Copper zirconium alloys |
>=85 | >=65 | Both of electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity are close to pure copper, the hardness is improved at normal temperature and high temperature than that of pure copper. (Heat-treated type alloy) |
It is recommended to aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, material covering metal(Each plating material of lead, silver, galvannealing, and cadmium), brass, and bronze. | 1 |
| Type 2 Chromium copper |
>=75 | >=75 | It is excellent in quality as resistance welding electrode, is generally in use. (Heat treatment type alloy) |
It is most widely recommended to soft steel, low-carbon steel, low electric conduction brass, bronze, galvanized steel, and stainless steel. | 2 |
| Type 3 Copper alloy including one element of beryllium, chromium, cobalt-nickel, silicon, or silver. |
>=45 | >=90 | It is recommended to a eccentric electrode holder with high usage rate and current energization mechanism parts that the stress is applied. (Heat treatment type alloy) |
It is generally recommended to spot welding for plate like a stainless steel, which has high electrical resistance. It is used to a tip, a base, an arm, and an adapter as electrode material. | 3 |
| Type 4 Beryllium copper |
>=20 | >=33(HRC) | Electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity are low, but it is excellent in hardness and tensile strength. Generally, it is not used as direct electrode. (Heat treatment type alloy) |
It is used for a shank of cap electrode, an adapter electrode arm, and L-type electrode holder in spot welding machine. It is used for electrode table which is needed mechanical strength in projection welding machine. | 4 |
| Type 5 Dispersion strengthened alloy |
>=75 | >=75 | Although electrical conductivity is close to that of pure copper, maintains high hardness close to the melting point. It is excellent in quality as resistance welding electrode material. | It is widely used for galvanized steel plate, stainless steel, including soft steel. It is excellent as a steel plate for surface treatment, comparing chromium copper up till now and chromium copper containing zirconium. Especially, adhesion is extremely few at the welding time. |
20 |
